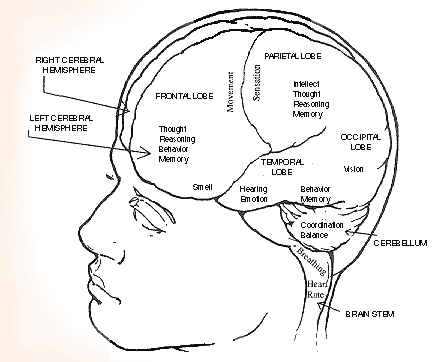
The brain controls the actions of the body and allows us to think, learn, and remember.
The brain has three main sections: the cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, and brain stem.
There are left and right cerebral hemispheres. The cerebral hemispheres are divided into sections called lobes. Each section of the brain has special jobs to do and sections of the brain also work together.
The left cerebral hemisphere controls the right side of the body and is usually responsible for speech. The right cerebral hemisphere controls the left side of the body and is usually responsible for creative thinking.
WHAT TYPES OF BRAIN INJURY MAY OCCUR?
Every injury is different. Most injuries are a result of bruising, bleeding, twisting, or tearing of brain tissue. Damage to the brain may occur at the time of injury. It may also develop after the injury due to swelling or further bleeding. Patients may have more than one type of brain injury.
SKULL FRACTURE:
a break in the bone that surrounds the brain. These fractures often heal on their own. Surgery may be needed if there has been damage to the brain tissue below the fracture.
CONTUSION/CONCUSSION:
a mild injury or bruise to the brain which causes a short loss of consciousness. A contusion or concussion may cause headaches, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and trouble remembering or concentrating. This injury will not need surgery.
COUP-CONTRA COUP:
a French word that describes contusions that occur at two sites in the brain. The force of the impact causes the brain to bump the opposite side of the skull. Damage occurs at the site of impact and on the opposite side of the brain.
EPIDURAL HEMATOMA:
a blood clot that forms between the skull and the top lining of the brain (dura). This blood clot can cause fast changes in the pressure inside the brain. Emergency surgery may be needed. The size of the clot will determine if surgery is needed.
SUBDURAL HEMATOMA:
a blood clot that forms between the dura and the brain tissue. If this bleeding occurs quickly it is called an acute subdural hematoma. If it occurs slowly over several weeks, it is called a chronic subdural hematoma. The clot may cause increased pressure and may need to be removed surgically.
INTRACEREBAL HEMORRHAGE:
a blood clot deep in the middle of the brain that is hard to remove. Pressure from this clot may cause damage to the brain. Surgery may be needed to relieve the pressure.
DIFFUSE AXONAL INJURY (DAI):
damage to the pathways (axons) that connect the different areas of the brain. This occurs when there is twisting and turning of the brain tissue at the time of injury. The brain messages get slowed or lost. Treatment is aimed at managing swelling in the brain because torn axons can not be repaired.
ANOXIC BRAIN INJURY:
an injury that results from a lack of oxygen to a part of the brain. This is most often from a lack of blood flow due to injury or bleeding. This will cause swelling of the brain tissue.
|
|
